
什么是睾丸扭转?
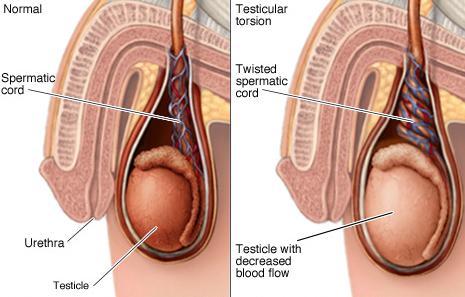
睾丸扭转是指睾丸和精索的扭转(精索是从腹股沟延伸到睾丸的结构,其中包含神经,输精管管和血管)。扭转引起到睾丸的血流减少,基本上扼杀了它们的氧气和营养。这是个疼痛的问题,通常会发生在10岁及以上的男孩。虽然它一般发生在青春期男孩,但也可能发生在胎儿发育过程中或婴儿出生之后不久。
什么原因引起睾丸扭转?
在青春期前和青春期的男孩,扭转主要起因于睾丸在阴囊内的不完全附着。这会使睾丸更有活动性,使得它们扭转。那些在胎儿时期被检测到的睾丸扭转,发生在当阴囊内围绕睾丸的保护性囊发育没有附着到阴囊内之时。
睾丸扭转的原因尚未可知。然而,已经看到一些发生在父亲,儿子,兄弟的案例,表明有遗传因素。
睾丸扭转的症状可能涉及一个或两个睾丸。以下是睾丸扭转的最常见症状。然而,每个孩子可能会经历不同的症状。症状可能包括:
· 阴囊的(累及阴囊):
o 疼痛
o 肿胀
o 在新生儿的瘀伤
o 在新生儿的硬块
o 发红
· 睾丸位置高
· 恶心和呕吐
· 提睾反射(参与控制睾丸运动进入盆腔的反射,正常情况下可由寒冷,触摸,情绪激动或锻炼引起)消失
睾丸扭转的症状可能类似于其他情况或医学问题。都需要咨询自己孩子的医生以求诊断。
睾丸扭转通常由体检和完整的病史获得诊断。医生也可以进行超声检查,这种无创性的检查是利用声波得到泌尿系统的图像,以评估睾丸的血流。一些医生也可以把具有典型症状的患儿直接送进手术室以求决定性的治疗。当务之急是作出迅速诊断,因为拖延的睾丸扭转可能会对睾丸造成不可逆转的损害。其他诊断性检查可能会有,但没有什么检查总是能够准确地诊断睾丸扭转的。
你孩子的医生将根据以下情况来确定睾丸扭转的具体处理:
· 你孩子的年龄,整体健康状况和病史
· 病情的程度
· 您孩子对具体药物、手术或治疗的耐受情况
· 对病情过程的预期
· 您的意见或倾向
睾丸扭转通常需要立即进行干预。扭转的严重程度取决于睾丸是部分性还是完全性扭曲。睾丸扭曲越严重,就越迫切需要干预。为了尽量减少长期的问题,通常需要在出现症状的6个小时之内进行干预。
大多数发生睾丸扭转的男孩需要及时手术来纠正这个问题。手术将有助于防止将来发生扭转。
睾丸扭转能否成功救治直接与缺血的发作的时间相关。如果在出现症状4 - 6小时内进行探查,抢救成功率可能接近90%;然而干预延迟,抢救成功率会急剧下降----在症状出现后12小时仅50%,而24小时后仅约10%。相比之下,围产期睾丸扭转几乎总是导致所涉及的睾丸丧失掉(抢救成功率< 5%)。
在一项调查中,55%的睾丸扭转男孩在阴囊探查时有梗死而丧失睾丸。睾丸丧失的主要原因是在寻求医疗帮助之前耽误了过多时间,通常归因于病人或他的父母。调查数据表明,大多数男孩不认为睾丸肿胀有就医必要,而且许多的老百姓也不认为睾丸肿胀和疼痛有就医必要。
Testicular Torsion
What is testicular torsion?
Testicular torsion is a twisting of the testicles and the spermatic cord (the structure extending from the groin to the testes that contains nerves, ducts, and blood vessels). The torsion causes decreased blood flow to the testes, essentially strangling them of oxygen and nutrients. This is a painful problem that usually occurs in boys age 10and older. While it generally occurs in adolescent boys, it may also occur during fetal development or shortly after a baby is born.
In preadolescent and adolescent boys, torsion occurs primarily from incomplete attachment of the testes within the scrotum. This permits the testes to be more movable, allowing them to twist. Testicular torsion detected in the fetus results when development of the protective sac that surrounds the testicles within the scrotum does not attach to the scrotum internally.
The cause of testicular torsion is unknown. However, some cases have been seen in fathers, sons, and brothers, suggesting a genetic component.
The symptoms of testicular torsion may involve one or both of the testes. The following are the most common symptoms of testicular torsion. However, each child may experience symptoms differently. Symptoms may include:
· Scrotal (involving the scrotum):
o Pain
o Swelling
o Bruising in newborns
o Firmness in newborns
o Redness
· High-lying testicles
· Nausea and vomiting
· Loss of cremasteric reflex (reflex involved in controlling testicular movement into the pelvic cavity, which is normally elicited by cold, touch, emotional excitement, or exercise)
The symptoms of a testicular torsion may resemble other conditions or medical problems. Always consult your child'sdoctor for a diagnosis.
Testicular torsion is usually diagnosed with a physical examination and a complete medical history. Your doctor may also perform an ultrasound, a noninvasive test that uses sound waves to make pictures of the kidney system to assess blood flow to the testicles. Some doctors may also take children with typical symptoms straight to the operating room for definitive treatment.It is imperative to make a prompt diagnosis because prolonged testicular torsion may cause irreversible damage to the testes. Other diagnostic tests may be included, but there is no test that can diagnose testicular torsion accurately all of the time.
Specific treatment for testicular torsion will be determined by your child'sdoctor based on:
· Your child's age, overall health, and medical history
· The extent of the condition
· Your child's tolerance for specific medications, procedures, or therapies
· Expectations for the course of the condition
· Your opinion or preference
Testicular torsion usually requires immediate intervention. The severity of the torsion depends on if the testicle(s) is partially or completely twisted. The more twisted the testicle, the more urgent the intervention. To minimize long-term problems, intervention is usually required within six hours of symptoms.
The majority of boys who develop testicular torsion will require prompt surgery to correct the problem. Surgery will help prevent torsion from occurring in the future.
Successful salvage of the torsed testis is directly related to the time elapsed from the onset of ischemia.If exploration is performed within 4-6 hours of symptom onset, salvage rates may approach 90%; with delayed intervention, however, these rates drop dramatically—to 50% at 12 hours after symptom onset and to almost 10% after 24 hours. In contrast, perinatal testicular torsion almost always results in loss of the involved testis (salvage rate < 5%).
In a survey, 55% of boys with testicular torsion had infarction with testis loss at scrotal exploration.The main reason for the testicular loss was excessive delay before seeking medical attention, usually attributed to the patient or his parents. Survey data have suggested that most boys do not think it is necessary to seek medical advice for testicular swelling, and a large minority do not think it is necessary to seek medical advice for testicular swelling with pain.
中山大学附属第一医院小儿外科
孙俊杰医生
Department of Pediatric Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-Sen University
Dr. SUN Junjie