
甲状舌管囊肿
· 什么是甲状舌管囊肿?
胚胎发育过程中,甲状腺也在发育,它起始于位于口腔后部舌根处的一组细胞。在胚胎发育过程中,甲状腺细胞经由一条管(被称为甲状舌管)下移,最终到达颈部甲状腺的位置。一旦甲状腺到达其最终位置,这条管道就退化,或消失。如果管道没有完全消失,在管道的多个部分就会形成囊袋,被称为甲状舌管囊肿。这些囊袋可充满液体或粘液。
· 症状
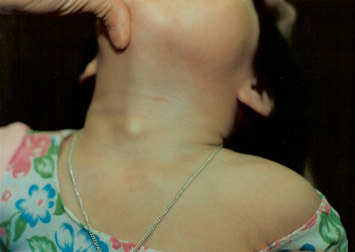
甲状舌管囊肿常常表现为在脖子前面正中有一个小圆形或椭圆形的包块或肿物。它们通常出现在学龄前到青春期的儿童。男女发病机会相同。囊肿可以随着时间变得更大,特别是患上呼吸道感染的孩子。有时候,巨大的囊肿可引起吞咽或呼吸困难。
甲状舌管囊肿可出现感染,引起囊肿区域的红肿和压痛。少见的情况是,囊肿形成穿破皮肤的窦道或开口,囊肿得以自我引流。在这些病例中,孩子们囊肿附近的皮肤上将有一个小开口,排出液体或粘液。这种情况并不多见,而且通常出现在感染发作之后。
· 评估和诊断
甲状舌管囊肿的诊断由病史和仔细的身体检查得出。你的孩子将有可能做超声检查来评估包块。
· 治疗
甲状舌管囊肿通常是通过手术来切除掉。然而,如果囊肿被感染,直至感染治愈后才能进行外科手术。没有对感染进行充足治疗的情况下,去切除一个受感染的囊肿,可能会导致手术非常困难。如果您的孩子患有受到感染的甲状舌管囊肿,在进一步手术切除之前,医生会开抗生素以治疗感染。
手术切除甲状舌管囊肿
切除甲状舌管囊肿的外科手术被称为Sistrunk手术,在全身麻醉下进行。
在囊肿上做一个小切口。囊肿和整条管道,以及舌骨的中间部分也都要被切除,舌骨就是在下巴下面颈部的一个小马蹄形骨。重要的是,囊肿和所附着的管道要完全切除。如果遗留一部分,囊肿很可能会复发,或回来。
任何被切除的组织都会送到病理实验室,以确认诊断。切口用可溶解缝线缝合。
手术后,你的孩子将在医院恢复到他或她病情稳定,能够毫不困难地吞咽。术后5-10天,伤口不应常规浸入水中(如游泳)。
· 随访
我们会安排您的孩子在手术后2-4周到外科门诊复诊。Sistrunk手术后复发率很低,但患者应进行监测,以确保病灶没有复发。
· 什么时候需要看医生
如果你的孩子有任何以下症状:
发热(38.5℃或以上)
任何感染的迹象,包括发红,肿胀或疼痛
切口有渗液
服了止痛药也不能控制的疼痛
在颈部正中的出现包块或肿状
任何进一步的问题或疑虑
Thyroglossal Duct Cyst
· What is a thyroglossal duct cyst?
When the thyroid gland is developing during embryological development, it starts out as a group of cells that are located at the base of the tongue in the back of the mouth. During embryological development, the thyroid cells move down a canal, called the thyroglossal duct, to the final location of the thyroid in the neck. Once the thyroid reaches its final location, the duct involutes, or disappears. If the duct does not fully disappear, portions of the duct can create pockets, called thyroglossal duct cysts. These pockets can fill with fluid or mucus.
· Symptoms
Thyroglossal duct cysts often present as small, round or oval masses or lumps in the center of the front part of the neck. They usually appear in preschool-aged children through adolescence. They affect males and females equally. The cysts can become larger over time, especially in children with an upper respiratory infection. Sometimes large cysts can cause difficulty swallowing or breathing.
Thyroglossal duct cysts can become infected, causing redness and tenderness in the area of the cyst. Rarely, the cysts create sinuses, or openings, to the skin through which the cysts drain on their own. In these cases, children will have a small opening in their skin near the cyst which drains fluid or mucus. This is uncommon, and typically follows an episode of infection.
· Evaluation and diagnosis
The diagnosis of a thyroglossal duct cyst is made by a health history and thorough physical exam. Your child will likely have anultrasoundto evaluate the mass.
· Treatment
Thyroglossal duct cysts are typically removed through surgical excision. However, if the cyst is infected, a surgical procedure should not be done until the infection is treated. Removing an infected cyst without adequately treating the infection can result in a more difficult surgery. If your child has an infected thyroglossal duct cyst, antibiotics will be prescribed to treat the infection before moving forward with surgical excision.
Surgery to remove thyroglossal duct cyst
The surgical procedure to excise a thyroglossal duct cyst is called the Sistrunk procedure and is performed under general anesthesia.
A small incision is made over the cyst. The cyst and the entire tract are removed, as well as the middle portion of the hyoid bone, a small horseshoe-shaped bone that is found in the neck below the chin. It is important that the cyst and the attached tract are completely removed. If a portion is left, the cyst has a higher likelihood of recurrence, or coming back.
Any tissue that is removed will be sent to the pathology lab to confirm the diagnosis. The incision will be closed with dissolvable sutures.
After surgery, your child will recover at hospital until he or she is stable and able to swallow without difficulty. The wound should not routinely be submerged under water (as in swimming) for 5-10 days.
· Follow-up care
We will schedule your child for a follow-up appointment with the surgery clinic 2-4 weeks after the procedure. Recurrence rates after a Sistrunk procedure are low, but patients should be monitored to ensure the lesion does not return.
· When to call the doctor
If your child has any of the following symptoms:
Fever (a temperature of 101.5 degrees or higher)
Any signs of infection, including redness, swelling or pain
Any drainage from the incision
Any pain that is not controlled with the prescribed pain medicine
A mass or lump in the center of the neck
Any further questions or concerns
中山大学附属第一医院小儿外科
孙俊杰医生
Department of Pediatric Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-Sen University
Dr. SUN Junjie